Wetenschap
Elektrofotokatalytische diaminatie van vicinale C-H-bindingen
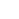
Elektrofotokatalytische aminering van C-H-bindingen. (A) Generieke elektrofotokatalytische cyclus met trisaminocyclopropenium (TAC) 1. (B) Ritter-type C-H amineringsreactie. (C) Elektrofotokatalytische vicinale CH-diamineringsreacties die in dit werk worden gerapporteerd. Sub, substraat; subox, geoxideerd substraat; Mij, methyl; en, ethyl; Ac, acetyl; Eox, oxidatiepotentieel; max, golflengte van maximale absorptie. Krediet:Wetenschap, 10.1126/science.abf2798
Anorganische scheikunde, de omzetting van geïnactiveerde koolstof-waterstof (C-H) bindingen naar koolstof-stikstof (C-N) bindingen is een zeer gewaardeerde transformatie. Wetenschappers kunnen dergelijke reacties op slechts één enkele C-H-plaats uitvoeren, aangezien de eerste derivatisering de reactiviteit van de omringende C-H-bindingen kan verminderen. In een nieuw rapport dat nu is gepubliceerd in Wetenschap , Tao Shen en Tristan H. Lambert bij de afdeling scheikunde en chemische biologie, Cornell universiteit, New York, toonde aan dat gealkyleerde arenen vicinale CH-diamineringsreacties konden ondergaan om 1 te vormen 2-diaminederivaten met behulp van een elektrofotokatalytische strategie. Tijdens het synthetische proces, ze gebruikten acetonitril als oplosmiddel en stikstofbron. Ze katalyseerden de reactie met behulp van een trisaminocyclopropenium (TAC) ion, die anodische oxidatie onderging om een stabiele radicaaldication (elk kation) te verschaffen, terwijl de kathodische reactie protonen reduceerde tot moleculaire waterstof. Toen ze de TAC-radicaalaanduiding bestraalden met een wit licht compact fluorescerend licht, ze genereerden een sterk oxiderend foto-geëxciteerd tussenproduct. Op basis van de gebruikte elektrolyt, het team behaalde ofwel 3, 4-dihydroimidazol- of aziridineproducten.
Een nieuw synthetisch proces
Alomtegenwoordige chemische reacties die inerte koolstof-waterstof (C-H) bindingen omzetten in waardevolle koolstof-stikstof (C-N) bindingen kunnen de constructie van complexe moleculen die relevant zijn voor de biomedische onderneming aanzienlijk versnellen. Onderzoekers hebben daarom een reeks C-H-amineringsreacties afgeleid, maar ondanks hun macht en reikwijdte, veel synthetische campagnes moeten talloze C-N-koppelingen installeren. Een grote uitdaging voor het ontwikkelen van dergelijke chemische reacties is dat heterofunctionaliteit de neiging heeft om omringende bindingen te deactiveren in de richting van de typische mechanistische modi van C-H-activering. Slechts een paar reactietechnologieën hebben daarom tot dusver multipotente functies op proximale C-H-bindingen verwezenlijkt. Shen et al. beschreef een strategie voor krachtige oxidatiechemie door de energie van licht en elektriciteit te combineren in een enkele katalysator in een proces dat bekend staat als elektrofotokatalyse (EPC). Tijdens deze strategie het team gebruikte elektrochemische oxidatie van trisaminocyclopropenium (TAC) -ionen onder een relatief milde elektrochemische potentiaal en gelijktijdige bestraling met zichtbaar licht om het resulterende radicale kationische tussenproduct te exciteren. De foto-geëxciteerde radicaaldication was een extreem krachtig oxidatiemiddel dat uitdagende reacties vertoonde, waaronder oxidatieve functies van benzeen en andere elektronenarme arenen of de regioselectieve CH-functionalisatie van ethers.
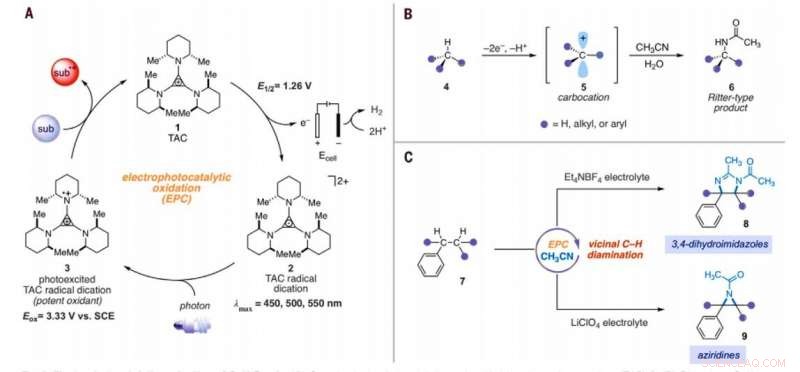
Substraatomvang van elektrofotokatalytische vicinale C-H-diaminatie. Alle opbrengsten zijn van geïsoleerde producten. Producten werden verkregen als racemische mengsels; wig- en streepjesafbeeldingen geven relatieve stereochemische relaties aan. (A) Diaminering van secundaire alkylbenzenen. (B) Diaminering van primaire alkylbenzenen. Experimentele details worden gegeven in de aanvullende materialen. Een asterisk geeft aan dat het op 2,2 V is uitgevoerd; een dolksymbool (†) geeft opwerking met NaHCO3 (aq) en CH3OH aan; en een dubbele dolk-dymbol (‡) geeft nBu4NPF6 aan in plaats van Et4NBF4. SM, startmaterialen. Verbinding 36 werd gedeacyleerd bij opwerken. Krediet:Wetenschap, 10.1126/science.abf2798 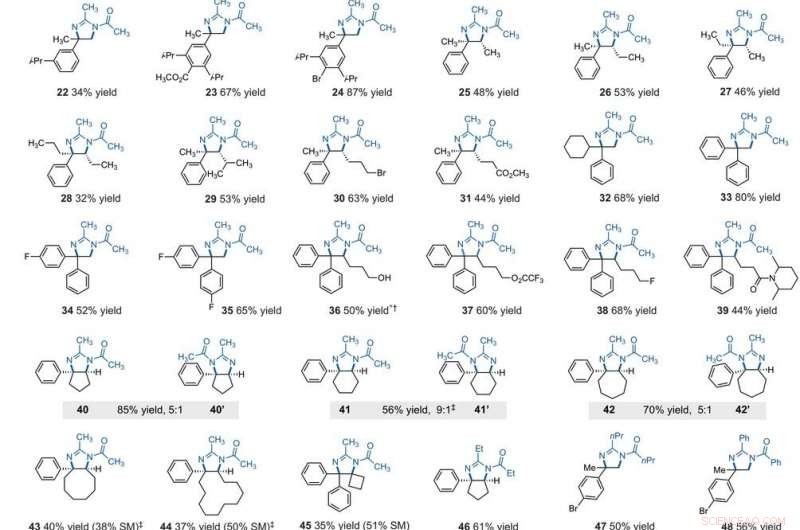
Het team veronderstelde dat de oxiderende kracht van TAC ook andere C-H-bindingsactiveringsverdeelstukken mogelijk maakt. Onder de juiste omstandigheden, de elektrofotokatalytische benadering zou carbo-kation-tussenproducten kunnen genereren om Ritter-type functionalisering van CH-bindingen te vergemakkelijken zonder een extern chemisch oxidatiemiddel. Typisch, tijdens Ritter-type reacties genereren een carbokation met daaropvolgende insluiting door een nitril om nitriliumion-tussenproducten te vormen, gevolgd door amideproducten na hydrolyse. Het team ging ervan uit dat de sterk oxiderende, maar selectieve omstandigheden aangeboden door TAC (trisaminocyclopropenium) EPC (elektrofotokatalyse) kunnen een reeks van meerdere Ritter-type C-H-functionalisatiereacties mogelijk maken, waarbij de aanvankelijk gevormde acetamidegroep een tweede amineringsreactie op een aangrenzende positie mogelijk maakte. Indien mogelijk, de methode zou de regioselectieve aminering van twee C-H-bindingen kunnen vergemakkelijken door eenvoudigweg zichtbaar licht te gebruiken, een milde elektrochemische potentiaal en een algemeen oplosmiddel als stikstofbron in plaats van nitreenprecursoren. Shen et al. reported the realization of the electrophotocatalytic deamination of C-H bonds to furnish dihydroimidazoles or aziridines, depending on the type of electrolyte used during the experiments.
Electrophotocatalytic vicinal C–H aziridination. Detailed reaction conditions for each substrate are provided in the supplementary materials. Products were obtained as racemic mixtures; wedge and dash depictions indicate relative stereochemical relationships. An asterisk indicates run at 2.2 V. i-Pr, isopropyl. Krediet:Wetenschap, 10.1126/science.abf2798
The synthetic products
After extensively screening, the reaction conditions including the cell potential, electrolyte, acid additive and reaction time, Shen et al. identified conditions to assist the efficient conversion of a variety of benzylic hydrocarbons of the corresponding N-acyl-4, 5-dihydroimidazole adducts. In the reaction setup, the scientists used visible light irradiation with a white compact fluorescent light of a solution of the substrate containing TAC in a divided electrolytic cell under controlled potential. The team added the TAC catalyst and substrate within the anodic chamber where the C-H deamination chemistry occurred. The resulting redox by-product was effectively traceless. Based on similar conditions, a variety of benzylic hydrocarbons underwent vicinal C-H diamination to form diverse products. In all cases, the researchers noted how the function of methylene carbons occurred in preference to methyl carbons, even when in the presence of a sterically demanding group or electron-withdrawing group. Since the α-α-diaryl amines formed a valuable substructure in biomedically relevant compounds, the team also investigated the transformation on gem-diaryl substrates. They found that the 1, 1-diphenyl ethane reacted efficiently to furnish a secondary alkyl benzene compound with 80 percent yield. The compatibility of alcohol, ester, alkyl fluoride and amide substituents allowed the synthesis of more highly functionalized adducts.
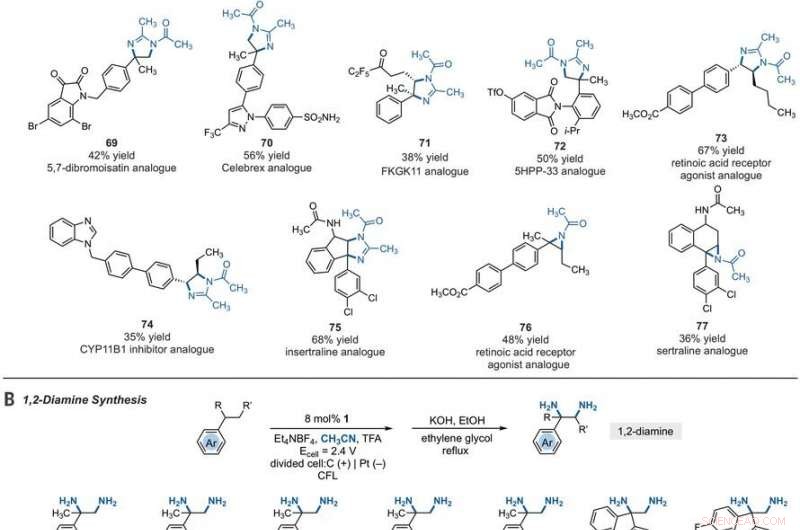
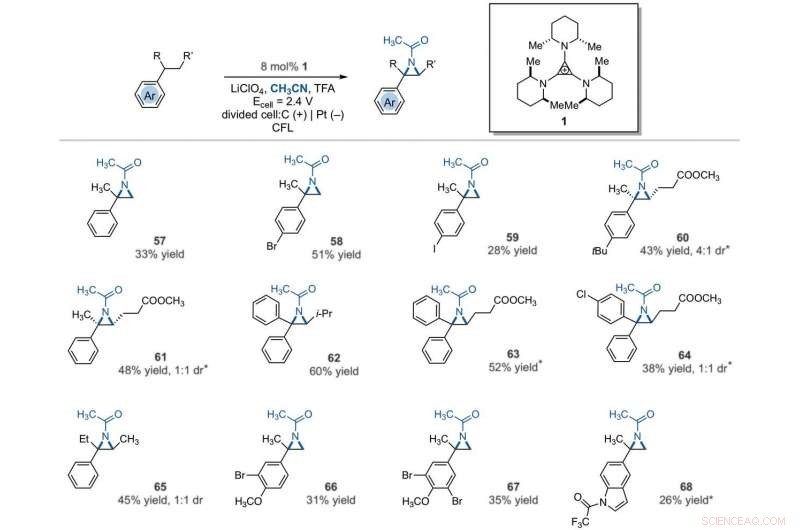
Synthetic applications of electrophotocatalytic vicinal C–H diamination. (A) Bioactive compound analogs prepared by means of electrophotocatalytic vicinal C–H diamination or aziridination. (B) 1, 2-Diamine synthesis. (C) Dihydroimidazole synthesis. (D) Bioactive compound synthesis. Detailed reaction conditions are provided in the supplementary materials. Products were obtained as racemic mixtures; wedge and dash depictions indicate relative stereochemical relationships. Products 80 and 81 were isolated as bis tosylate salts. Ph, fenyl; Tf, trifluoromethanesulfonate. Krediet:Wetenschap, 10.1126/science.abf2798
Functionalizing ring systems
The team further studied the potential of this reaction to functionalize ring systems. The reaction of phenyl cyclopentane led to the bicyclic compound in 85 percent yield. The scientists produced six- and seven-membered ring products as regioisomeric mixtures, alongside eight- and 12-membered ring products as single isomers. They improved some of the yields for cyclic substrates by using tetrabutylammonium phosphate (TBAF 6 ) as the electrolyte. In addition to acetonitrile, the researchers used other nitriles to give rise to diaminated products derived from propionitrile, butyl nitrile or benzonitrile as the nitrogen source. The scientists also tested the diamination process using unbranched benzylic substrates. Als resultaat, imine and halogenated derivatives gave rise to aziridines in low to modest yields with nearly equal yields of diaminated products.
Mechanistic rationale for electrophotocatalytic vicinal C–H diamination. Voltages were measured in a 5:1 mixture of CH3CN and TFA to mimic the reaction conditions and are relative to SCE. Krediet:Wetenschap, 10.1126/science.abf2798 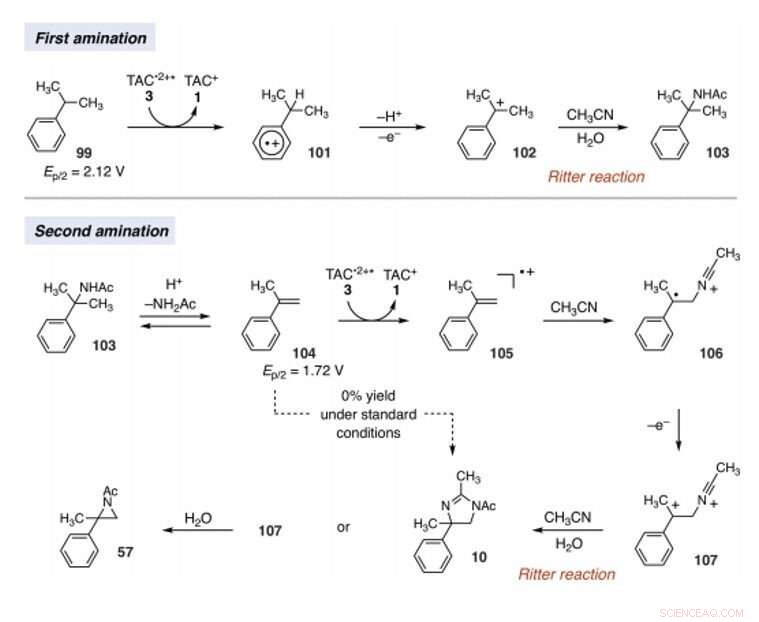
Since late-stage C-H functionalization processes offered powerful tools for the diversification of medicinal compound libraries, Shen et al. tested the difunctionalization chemistry on several molecules that are close analogs of known biologically active molecules. The team diaminated a dibromoisatin derivative to produce a bioactive molecule analogue in 42 percent yield. Bijvoorbeeld, Isatin derivatives have been investigated in the past due to their medicinal properties including antitumor and antiviral activities. The scientists also found that celecoxib analogs could produce 56 percent yield under standard conditions. They then converted an analog of thalidomide with antiproliferative activity into another bioactive analog with 50 percent yield. The team further found how a small modification to the electrophotocatalytic procedure could lead to the isolation of free 1, 2-diamines in good yields. Shen et al. believe the mechanisms to have originated with Ritter-type amination of the substrates benzylic C-H bond in a process that accords with known electrochemical Ritter-type reactions. Op deze manier, Tao Shen and Tristan H. Lambert noted the compatibility of deamination with a reasonable diversity of functionality for the practical applications of this reaction. The scientists used the power of combined light and electrical energy to conduct the reactions in the functionality of a single catalyst with advancing synthetic capabilities.
© 2021 Science X Network
 Onderzoekers delen strategieën om geowetenschappen inclusiever te maken
Onderzoekers delen strategieën om geowetenschappen inclusiever te maken Wat zijn de bronnen van het Amazone-regenwoud?
Wat zijn de bronnen van het Amazone-regenwoud?  Door de opwarming van de aarde is het risico op ernstigere droogtes in Kaapstad al toegenomen
Door de opwarming van de aarde is het risico op ernstigere droogtes in Kaapstad al toegenomen NASA's Suomi NPP-satelliet toont twee weergaven van de rokerige luchten van Californië
NASA's Suomi NPP-satelliet toont twee weergaven van de rokerige luchten van Californië Daling van begrazingspraktijken bedreigt het bestaan van een Baskische kaas
Daling van begrazingspraktijken bedreigt het bestaan van een Baskische kaas
Hoofdlijnen
- Moderne celtheorie
- Waarom gifkikkers zichzelf niet vergiftigen?
- Herprogrammering van buiten naar binnen:antilichaamonderzoek suggereert een betere manier om stamcellen te maken
- Waarom is chemie belangrijk voor de studie van anatomie en fysiologie?
- Doden lindebomen bijen?
- Lichaamsdelen en functies
- Inspanningen van de marine om walvissen te beschermen hebben beperkt effect
- Waar vindt glucoserosorbtie plaats?
- Insectengedrag bestuderen? Maak van jezelf een ethoscoop
- Ontwikkeling van multifunctionele composietmaterialen voor ruimtevaarttoepassingen
- Molfracties berekenen met massapercentage

- Verbetering van de kristalgroei met behulp van polyelektrolytoplossingen en afschuifstroming
- De natuur biedt routekaart voor mogelijke doorbraken in zonne-energietechnologie

- Lichaamswarmte benutten om elektronische apparaten van stroom te voorzien

 Denk je dat je slecht bent in wiskunde? Je kunt last hebben van wiskundetrauma
Denk je dat je slecht bent in wiskunde? Je kunt last hebben van wiskundetrauma Franse drone-maker Parrot schrapt meer banen als verkoopneusduik
Franse drone-maker Parrot schrapt meer banen als verkoopneusduik Studie vindt meteorisch bewijs voor een voorheen onbekende asteroïde
Studie vindt meteorisch bewijs voor een voorheen onbekende asteroïde Spinstroom op topologische isolator elektrisch gedetecteerd bij kamertemperatuur
Spinstroom op topologische isolator elektrisch gedetecteerd bij kamertemperatuur Helpt het antiparasitaire medicijn te verminderen
Helpt het antiparasitaire medicijn te verminderen Kepler-telescoop bespioneert details van de buitenste planeet van het TRAPPIST-1-systeem
Kepler-telescoop bespioneert details van de buitenste planeet van het TRAPPIST-1-systeem Klimaatverandering zal de komende decennia miljoenen verdringen - landen moeten zich nu voorbereiden om hen te helpen
Klimaatverandering zal de komende decennia miljoenen verdringen - landen moeten zich nu voorbereiden om hen te helpen Harmonisatie van bosinformatie zet een stap voorwaarts in Europa:gedeelde praktijken toegepast in meer dan 20 landen
Harmonisatie van bosinformatie zet een stap voorwaarts in Europa:gedeelde praktijken toegepast in meer dan 20 landen
- Elektronica
- Biologie
- Zonsverduistering
- Wiskunde
- French | Italian | Spanish | Portuguese | Swedish | German | Dutch | Danish | Norway |
-
Wetenschap © https://nl.scienceaq.com