Wetenschap
Op plasma-ionisatie gebaseerde 3D-titania nanovezelachtige webben om de bioreactiviteit en osteogeleiding van biomaterialen te verbeteren
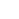
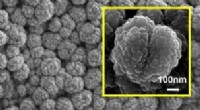
Schematische mechanismen van celproliferatie en osteo-inductiviteit van nanovezelachtige titaniumcoating door oppervlaktemodificatie door laser-geïnduceerde omgekeerde overdracht met hoge intensiteit (HILIRT):een nieuwe afzettingsmethode. (a) NFTi-laag afgezet op glas door de voorgestelde HILIRT-techniek bij laserstraalscansnelheden. (b) De biocompatibiliteit van titanium als implantaatmateriaal wordt toegeschreven aan oppervlakteoxide dat spontaan wordt gevormd in lucht en/of fysiologische vloeistoffen, en men gelooft dat cellulair gedrag, bijv. hechting, verspreiding en proliferatie worden sterk beïnvloed door 1. Oppervlakte 2. bevochtigbaarheid 3. hydroxylgroepen aan het oppervlak (de hydroxylgroepen aan het oppervlak van terminale OH- reguleren het initiële eiwitadsorptiegedrag). (c) Oppervlakte-hydroxylgroepen en bioactieve Ti-nanodeeltjes bevorderen osteoblastdifferentiatie door 1. De Ti-OH-groepen gevormd op het oppervlak van titanaat na onderdompeling in osteogeen kweekmedium zijn negatief geladen, en dus selectief combineren met de positief geladen Ca2+-ionen in de vloeistof om uiteindelijk calciumfosfaat te vormen. 2. Biocomplexen (ionen, eiwit en groeifactor) worden geïnternaliseerd door caveolae-gemedieerde endocytose. (d) Perspectief:botvorming en hermodellering rond geïmplanteerde materialen. Krediet:wetenschappelijke rapporten, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-54533-z
In een nieuwe studie gepubliceerd op Wetenschappelijke rapporten , Mohammad-Hossein Beigi en een onderzoeksteam van de afdelingen Engineering and Applied Science en Cellular Biotechnology in Canada en Iran hebben een nieuwe methode beschreven om biocompatibele biomaterialen te vormen voor botweefselengineering. Ze ontwikkelden webachtige, driedimensionale (3-D) Titania nanovezelcoatings met behulp van laser-geïnduceerde omgekeerde overdracht met hoge intensiteit (HILIRT). Het team demonstreerde eerst het mechanisme van ablatie en titanium (Ti)-afzetting op glassubstraten met behulp van meerdere picoseconde laserpulsen in omgevingslucht om theoretische voorspellingen te vergelijken met experimentele resultaten. Ze onderzochten de prestaties van glasmonsters die zijn ontwikkeld door titanium nanovezelstructuren te coaten door middel van verschillende laserpulsduur, met behulp van methoden zoals scanning elektronenmicroscopie (SEM).
Om de interacties tussen het nieuwe materiaaloppervlak en biologische cellen te begrijpen, Beigi et al. onderzocht interacties van menselijke bot-afgeleide mesenchymale stamcellen (BMSC's) gekweekt op de nieuwe biomaterialen. Voor deze, ze gebruikten een verscheidenheid aan in-lab-tests, waaronder een colorimetrische methode om de metabolische activiteit van cellen te begrijpen (MTS-assay), immunocytochemie, eiwitadsorptie- en absorptieanalyses. De resultaten toonden een significant verbeterde biocompatibiliteit in met laser behandelde monsters in vergelijking met onbehandelde substraten. Beigi et al. wijzigden hun HILIRT-techniek door de pulsduur te verkorten en titanium nanovezels met dichtere structuren te genereren tijdens geavanceerde materiaaltechnologie. Volgens hun bevindingen de dichtheid van nanostructuren en de concentratie van gecoate nanovezels speelden een cruciale rol bij het genereren van bioactiviteit in de behandelde monsters door vroege differentiatie van BMSC's (botafgeleide mesenchymale stamcellen) te induceren om botweefsel te vormen via osteogene differentiatie (botvorming).
Bio-ingenieurs ontwikkelen snel nieuwe technieken voor botweefselengineering (BTE) voor botregeneratie; om de bestaande "gouden standaarden" van bot-autograft- en allograft-methoden in de regeneratieve geneeskunde te verbeteren. Nadelen van de bestaande technieken zijn onder meer morbiditeit op de donorplaats en beperkte voedingssupplementen tijdens botregeneratie. Bone tissue engineering (BTE) is een veelbelovende onderzoeksrichting om botgroei en -herstel te vergemakkelijken, zelfs bij grootschalige skeletafwijkingen. Onderzoekers streven ernaar om stamcellen met AHO te gebruiken vanwege hun zelfvernieuwende mogelijkheden naast stamceldifferentiatie, om verschillende weefseltypes te vormen. Aangezien de fysische en chemische eigenschappen van een materiaaloppervlak de levensvatbaarheid van menselijke mesenchymale stamcellen (hMSC's) voor zelfherstel kunnen beïnvloeden, differentiatie en proliferatie. Materialen en cellen kunnen daarom samenwerken in toepassingen van AHO om een gewenst platform te bieden voor osseo-integratie tijdens botremodellering.
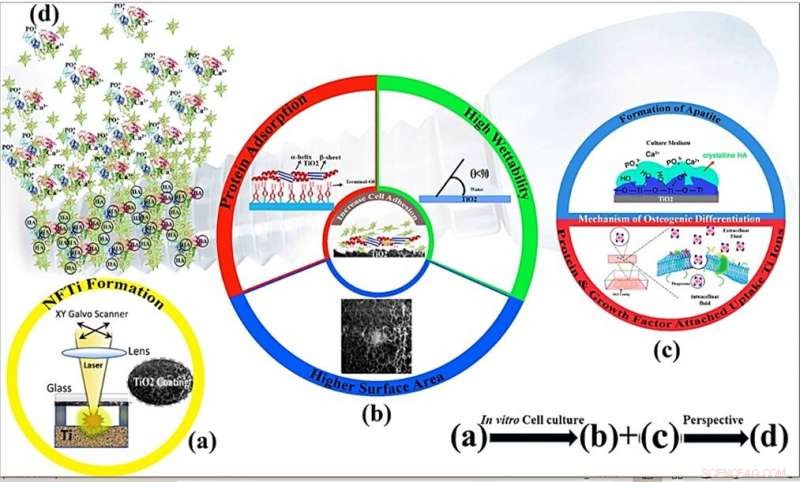
BOVEN:SEM-beelden van NFTi-laag (Nanovezelige Titania) met vermogen = 10 W, frequentie = 600 KHz (a) pulsduur = 150 ps, (b) pulsduur = 5 ns, (c) pulsduur = 30 ns met 50000X vergroting. ONDER:(a) XRD-patroon, (b) Raman-spectrum van kaal glas en monsters gecoat door titania met verschillende pulsduur (gemaakt door Origin Pro 2019B (GF3S4-3089-7907079) https://www.originlab.com/). Krediet:wetenschappelijke rapporten, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-54533-z.
Onderzoeksteams hadden eerder verschillende technieken gebruikt om AHO-materiaaloppervlakken te produceren, waaronder sol-gel, hydrothermisch 106, elektrospinnen en 3D-printen; echter, het kiezen van een ideale methode blijft een uitdaging. Bijvoorbeeld, kunstmatige biomaterialen moeten moeiteloos interageren met fysiologische vloeistoffen en assimileren met harde en zachte omringende weefsels om cellulaire activiteit te behouden voor superieure biocompatibiliteit. Materiaalwetenschappers en bio-ingenieurs hadden titanium en zijn legeringen gebruikt voor orthopedische implantaten, waardoor op titanium nanodeeltjes (NP) gebaseerde osteogenese van tandpulpstamcellen en van vetweefsel afgeleide stamcellen mogelijk wordt. Methoden voor het modificeren van laseroppervlakken kunnen materiaaloppervlakken wijzigen voor verbeterde biocompatibiliteit van het oppervlak; waar de HILIRT-methode eerder potentieel had getoond om lab-on-a-chip-componenten en andere biocompatibele biomaterialen te ontwikkelen. Wetenschappers kunnen laserparameters wijzigen om materiaaloppervlakken te manipuleren om celdifferentiatie te ondersteunen.
In het huidige werk, Beigi et al. onderzocht effecten van laserpulsduur op materiaaloppervlakken met behulp van de HILIRT-methode en testte het biologische gedrag van synthetische biomaterialen met behulp van materiaalkarakterisering en biologische tests in het laboratorium. Ze onderzochten cel-materiaal contact op materiële oppervlakken met behulp van genexpressie, mineralisatie en eiwitinteractiestudies. De wetenschappers ontwikkelden een nanovezelachtige titania (NFTi) dunne film en dompelden deze in gesimuleerde lichaamsvloeistof (SBF) om hydroxyapatiet (HA)-achtige laagstructuren te vormen en identificeerden de materiële oppervlaktemodificaties met behulp van de watercontacthoek (CA), scanning elektronenmicroscopie (SEM), energiedispersieve röntgenspectroscopie (EDS) analyse, micro-Raman en röntgendiffractie (XRD) spectroscopieën.
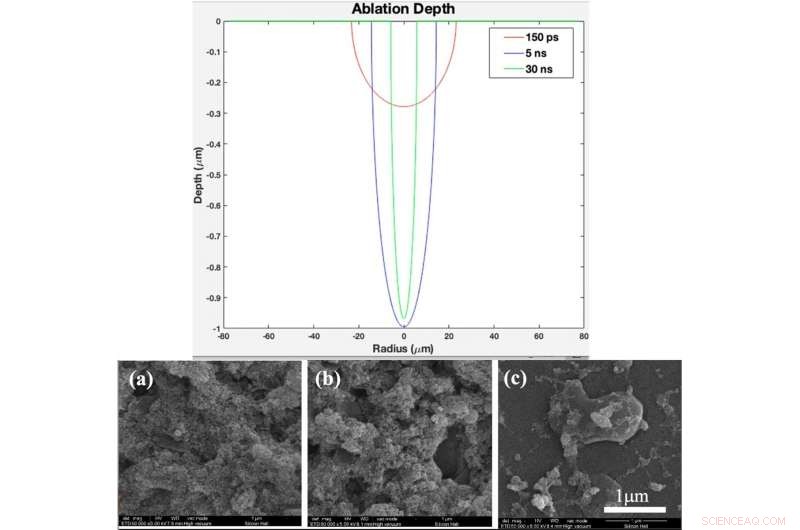
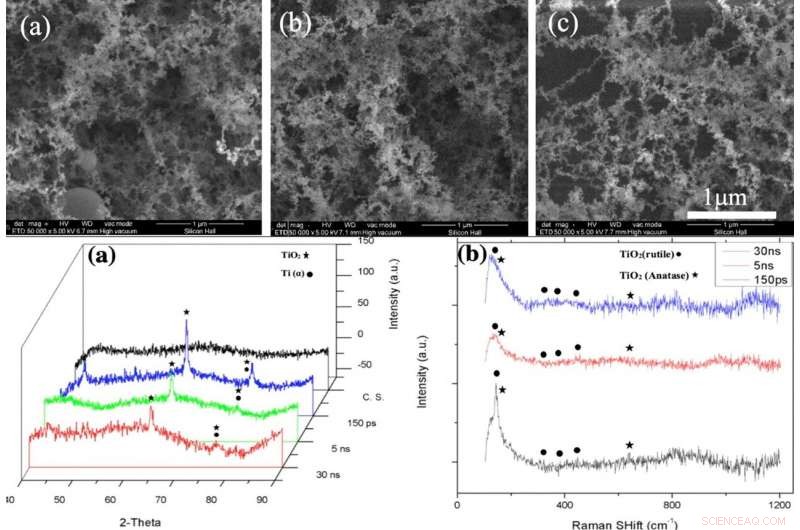
BOVEN:Theoretisch ablatiediepteprofiel als functie van straal voor pulsduur van 150 ps, 5 ns, and 30 ns (created in MATLAB R2015b software (9.6.0.1072779) https://www.mathworks.com). BOTTOM:(a) XRD pattern, (b) Raman spectrum of bare glass and samples coated by titania with different pulse durations after 2 days immersion in SBF, (c) XRD pattern, (d) Raman spectrum of bare glass and samples coated by titania with different pulse duration after 4 days immersion in SBF Fig. 4. (a). XRD pattern, (b) Raman spectrum of bare glass and samples coated by titania with different pulse durations (created by Origin Pro 2019B (GF3S4-3089-7907079) https://www.originlab.com/). Krediet:wetenschappelijke rapporten, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-54533-z.
They deposited NFTi (nanofibrous titania) structures at different pulse durations to form laser nanofiber coated smooth surfaces and tested the chemical and physical composition of the resulting advanced materials. When they decreased pulse duration, the titanium weight percentage increased, and the scientists observed the temperature of the irradiated zone to be significantly higher for a shorter pulse duration of 150 picoseconds (ps) compared with 5 nanoseconds (ns) and 30 ns. The decreased pulse duration transmitted power to the target in a shorter time, causing the heat affected zone (HAZ) to have a higher temperature, allowing a denser plasma plume to form more NFTi structures on a glass substrate. Decreasing the laser pulse duration created more biocompatible Ti nanofibers with a higher content of HA(hydroxyapatite)-like substance sedimentation on the samples.
Using phase-contrast microscopy images of fibroblast-like BMSCs on titania-coated glass surfaces, Beigi et al. observed normal cell morphology. They measured water contact angles of droplets of water on the material specimens and conducted cytotoxicity tests with MTS assays on stem cells grown on NFTi coatings. The materials coated with NFTi for 150 ps showed the highest absorbance rate (known as the S1 group) with subsequently high rates of cell viability, cell adhesion and metabolic activity. When the researchers used immunofluorescent staining to observe cell migration, the S1 sample (with NFTi coating for 150 ps) showed higher rates of cell migration. To confirm stem cell (BMSC) differentiation, the scientists investigated osteogenic-related gene expression with RUNX2, collagen I, osteopontin and osteonectin genes, using quantitative qRT-PCR. Onder de monsters, S1 samples indicated significantly higher relative expression for all osteogenic-related genes.
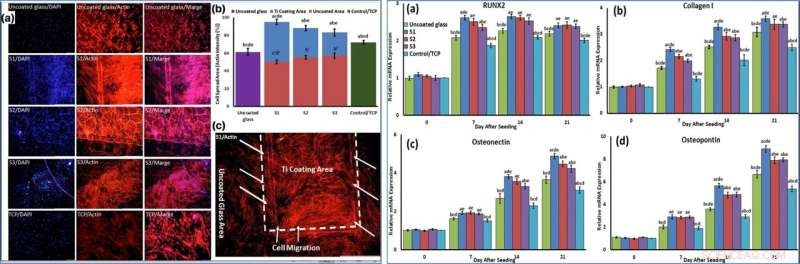
LEFT:Cells were stained by phalloidin to observe (a, c) and quantify (b) actin filament expansion and migration in all samples after 7 days. The first column in A is DAPI nuclear staining (blue), second column, phalloidin labelled F-actin (red), and third column, overlaid fluorescent image of immunostained cellular components (merge:DAPI/F-actin). The red bars in B indicate the intensity percentage of actin filament on the glass in S1, S2, and S3 samples and the blue bars describe the intensity percentage of actin filament the NFTi coated area. (c) Higher magnification of BMSCs migration from glass area toward Ti coating area in S1. RIGHT:The mRNA relative expression levels of osteogenic genes included Runx2 (a), Collagen I (b), Osteonectin (c), and Osteopontin (d) determined by qRT-PCR for all samples. Krediet:wetenschappelijke rapporten, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-54533-z.
To confirm mineralization, the scientists used alizarin red followed by soluble Ca nodules color absorbance quantification, to observe high levels of mineralization on all samples on days seven and 14. The team investigated surface protein absorption potential, protein-ion biocomplex formation and biocomplex cell uptake to demonstrate highest levels of protein-ion biocomplex formation on the S1 samples.
Op deze manier, Mohammad-Hossein Beigi and colleagues used the HILIRT method to achieve high surface bioreactivity, osteogenesis and osseointregration of NFTi-BMSCs. The surface character of the new materials allowed protein and biomolecule interactions to stimulate cell adhesion, mineralization and osteogenesis for faster and more suited osseointegration in vivo and in vitro. The scientists engineered nanofiber mesh-like scaffolds using titanate to allow vascularization, protein attachment, cell proliferation and cell attachment on the substrate. Such microporous surfaces can promote nutrition diffusion, vascularization and blood flow due to improved biomechanical strength. In aanvulling, the hydrophilic surface property; verified using water contact angle measurements, facilitated cell-ECM adhesion to improve cell binding and vigorous tissue growth.
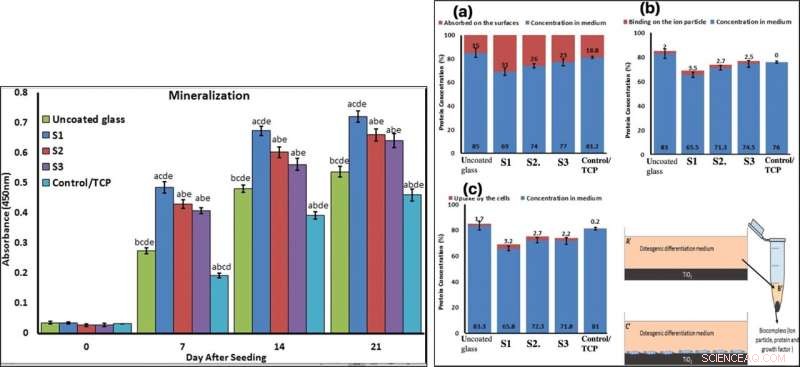
LEFT:Confirmation of osteogenic differentiation and matrix mineralization of BMSCs by quantifying alizarin red staining. RIGHT:Protein adsorption and biocomplex adsorption/absorption:concentration of protein in osteogenic differentiation medium after 6 hours of immersion (a); concentration of protein in osteogenic differentiation medium after 6 hours of immersion and then centrifuged at 14, 000 rpm for 30 min (b); concentration of protein in osteogenic differentiation medium after 6 hours of immersion with cell culture (c). Krediet:wetenschappelijke rapporten, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-54533-z.
The S1 sample (NFTi, 150 ps) developed in this work generated the best surface bioreactivity for bone regeneration or bone replacement. Beigi et al. showed the advantages of using titania as an orthopedic implant material and the surface modification strategies implemented in the study improved surface bioreactivity and osteogenesis for assisted bone tissue development. The cost-effective frugal method can provide a metallic nanofiber structure surface to be coated on multiple surfaces for varied biomedical applications. The proposed technique (combining materials engineering with stem cells) will open new doors to engineer advanced biomaterials with enhanced surface bioreactivity for improved biocompatibility in vitro and in vivo. The findings demonstrate beneficial effects of an experimental scaffold in the lab with potential for medical osseointegration as a BTE implant.
© 2019 Wetenschap X Netwerk
 Fagen gebruiken om nieuwe antivries-eiwitten te ontdekken
Fagen gebruiken om nieuwe antivries-eiwitten te ontdekken Niet-toxische onderwaterlijm kan nieuwe chirurgische lijm opleveren
Niet-toxische onderwaterlijm kan nieuwe chirurgische lijm opleveren Katalysator maakt reacties mogelijk met behulp van groen licht
Katalysator maakt reacties mogelijk met behulp van groen licht Designerbacteriën produceren koraalantibioticum
Designerbacteriën produceren koraalantibioticum De gevoelige spanningssensor die het gewicht van een veer kan detecteren
De gevoelige spanningssensor die het gewicht van een veer kan detecteren
 Indiase hoofdstad stikt in ernstige smog terwijl boerderijbranden toenemen
Indiase hoofdstad stikt in ernstige smog terwijl boerderijbranden toenemen NASA's GPM vindt zware regenval op de zuidwestelijke kant van de tropische storm Prapiroons
NASA's GPM vindt zware regenval op de zuidwestelijke kant van de tropische storm Prapiroons Omslagpunt klimaatverandering kan sneller komen dan we denken:studie
Omslagpunt klimaatverandering kan sneller komen dan we denken:studie Wereldwijd rapport over plastic bedreigingen voor de oceaan
Wereldwijd rapport over plastic bedreigingen voor de oceaan Nieuw rapport zegt dat het versnellen van de wereldwijde groei van de landbouwproductiviteit van cruciaal belang is
Nieuw rapport zegt dat het versnellen van de wereldwijde groei van de landbouwproductiviteit van cruciaal belang is
Hoofdlijnen
- Hoe bekritiseer je iets zonder een eikel te zijn?
- Hoe orchideeën werken
- Celcontacten in embryonale ontwikkeling bepalen cellulair lot
- Is het DNA tussen genen echt rommel?
- Synthetische seks in gist belooft veiligere medicijnen voor mensen
- Kan een naaimachine DNA aan elkaar naaien?
- Update over bedreigde Filippijnse cycadsoorten
- Hoe beïnvloedt stress je hersens?
- Een onwaarschijnlijke held vergiftigen bij het afweren van exotische indringers?
- Koolstof nanobuisjes kweken met de juiste twist
- Boornitride is een veelbelovende weg naar praktische grafeenapparaten

- Niet langer alleen een toeschouwer, siliciumoxide komt in de elektronica-actie op computerchips

- Zeer geleidende germanium nanodraden gemaakt door een eenvoudige, proces in één stap
- Ontwikkeling van silicium-metaalcomposietmateriaal voor oplaadbare lithium-ionbatterijen met hoge capaciteit
 Wat wordt geoxideerd en wat wordt gereduceerd in celademhaling?
Wat wordt geoxideerd en wat wordt gereduceerd in celademhaling?
Tijdens aerobe ademhaling, combineert de zuurstof die een cel inneemt met glucose om energie te produceren in de vorm van Adenosine-trifosfaat (ATP), en de cel verdrijft koolstofdioxid
 5 kenmerken die alle vissen gemeen hebben
5 kenmerken die alle vissen gemeen hebben  Nieuw model voorspelt nauwkeurig hoe kusten worden beïnvloed door stormen en zeespiegelstijging
Nieuw model voorspelt nauwkeurig hoe kusten worden beïnvloed door stormen en zeespiegelstijging Het oog van de piloot volgen
Het oog van de piloot volgen Lokale symmetrie doorbreken - waarom water bevriest maar silica een glas vormt?
Lokale symmetrie doorbreken - waarom water bevriest maar silica een glas vormt? Hoe kevers te identificeren in Ontario, Canada
Hoe kevers te identificeren in Ontario, Canada  Milieuproblemen en -oplossingen
Milieuproblemen en -oplossingen NASA-rover neemt monsters van actieve lineaire duin op Mars
NASA-rover neemt monsters van actieve lineaire duin op Mars
- Elektronica
- Biologie
- Zonsverduistering
- Wiskunde
- French | Italian | Spanish | Portuguese | Swedish | German | Dutch | Danish | Norway |
-
Wetenschap © https://nl.scienceaq.com