Wetenschap
How does a rotary-type rheostat work?
Structuur:
* Resistive Element: A long, thin strip of resistive material (like wirewound, carbon, or conductive plastic) is wound around a cylindrical form. This element forms a continuous path for current to flow.
* Rotating Contact (Wiper): A movable contact, often called a wiper, is attached to a shaft that can be rotated. This contact rides on the resistive element.
* Fixed Contacts: Two fixed contacts are connected to the ends of the resistive element, providing a reference point for the circuit.
Operation:
1. stroomstroom: Wanneer de stroom het circuit binnenkomt, stroomt het door een van de vaste contacten, door het resistieve element, en verlaat het door het andere vaste contact.
2. Variable Resistance: As the wiper rotates, it moves along the resistive element. This changes the length of the resistive element that the current must flow through, thereby changing the resistance.
3. Voltage Division: The wiper also divides the voltage applied across the resistive element. The voltage between the wiper and one of the fixed contacts varies depending on the wiper's position.
How it Works:
* Increasing Resistance: Wanneer de wisser naar één vast contact beweegt, neemt de lengte van het resistieve element waar de stroom doorheen stroomt, waardoor de weerstand wordt verhoogd.
* Decreasing Resistance: Wanneer de wisser naar het andere vaste contact beweegt, neemt de lengte van het resistieve element dat de stroom doorheen stroomt af, waardoor de weerstand afneemt.
Toepassingen:
Rotary rheostats find extensive use in various applications, including:
* Volume Control: In audio systems, they adjust the volume by varying the resistance, controlling the signal strength.
* Speed Control: In motors, they can control speed by changing the resistance in the motor's armature circuit.
* Dimming Lights: By adjusting the resistance in the circuit, they control the brightness of light bulbs.
* sensoren: They are used in various sensors to detect changes in position, pressure, or temperature.
Voordelen:
* Eenvoudig ontwerp: Rotaire reostaten zijn relatief eenvoudig in ontwerp en constructie.
* Duurzaam: They are generally quite durable and can handle significant current loads.
* Gladde controle: They provide smooth and continuous control over the resistance, making them suitable for applications requiring gradual adjustments.
Nadelen:
* Draag: Na verloop van tijd kan het contact tussen de ruitenwisser en het resistieve element verslijten, wat verhoogde ruis of weerstandsschommelingen veroorzaakt.
* Beperkte resolutie: Voor toepassingen met een hoge precisie kunnen ze niet voldoende oplossen in weerstandsveranderingen.
* stroomverbruik: Sommige reostaten kunnen aanzienlijk vermogen verbruiken, met name bij lage weerstandsinstellingen.
In moderne elektronica worden roterende reostaten vaak vervangen door potentiometers of digitale potentiometers die vergelijkbare functionaliteit bieden met een grotere nauwkeurigheid en minder slijtage. Rotaire reostaten worden echter nog steeds op grote schaal gebruikt in sommige toepassingen vanwege hun eenvoud, duurzaamheid en kosteneffectiviteit.
Hoofdlijnen
- Generaal Sherman slaagt voor de gezondheidscontrole, maar 's werelds grootste bomen worden geconfronteerd met toenemende klimaatbedreigingen
- Hoe diabetes werkt
- Wat is ATP en waarom het belangrijk is voor het metabolisme?
- Op welke twee Griekse woorden is fotosynthese gebaseerd?
- Insecten kunnen mensen leren omgaan met tegenslag
- Hoe mensen uit het stenen tijdperk de glucose in planten ontsloten
- Waarom worden insectieve planten gedeeltelijke parasieten genoemd?
- Welke vier items maken een eiwit?
- Het Bohr-model:snel vervangen maar nooit vergeten
- Een diepe duik in het binnenland van rode dwergen

- Eerste experimentele waarneming van nieuw type verstrengeling in een 2D-kwantummateriaal

- De realisatie van een single-quantum-dot warmteklep
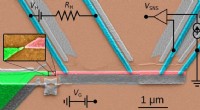
- Natuurkundigen gebruiken extreme infrarood laserpulsen om bevroren elektronengolven in magnetiet te onthullen

- Röntgenstralen geven aan dat water zich kan gedragen als een vloeibaar kristal
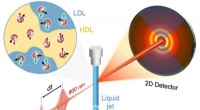
 Insecten of stof? Nieuwe methode laat snel zien of een oppervlak echt schoon is
Insecten of stof? Nieuwe methode laat snel zien of een oppervlak echt schoon is Wat gebeurt er als er niet genoeg wrijving is?
Wat gebeurt er als er niet genoeg wrijving is?  Welke plaat -trek beschrijft?
Welke plaat -trek beschrijft?  Houden niet-leuke schimmels kunstmest van planten?
Houden niet-leuke schimmels kunstmest van planten? Hoe een badkamer in één dag 3D te printen?
Hoe een badkamer in één dag 3D te printen? De bouwstenen van het leven zijn verrassend stabiel in Venus-achtige omstandigheden:studie
De bouwstenen van het leven zijn verrassend stabiel in Venus-achtige omstandigheden:studie  De meeste Amerikanen kiezen tegenwoordig voor crematie. Waarom begrafenissen steeds minder gebruikelijk zijn
De meeste Amerikanen kiezen tegenwoordig voor crematie. Waarom begrafenissen steeds minder gebruikelijk zijn  Facebook bouwt een besturingssysteem voor toekomstige apparaten
Facebook bouwt een besturingssysteem voor toekomstige apparaten
- Elektronica
- Biologie
- Zonsverduistering
- Wiskunde
- French | Italian | Spanish | Portuguese | Swedish | German | Dutch | Danish | Norway |
-
Wetenschap © https://nl.scienceaq.com