Wetenschap
Een bepaalde massa koolstof reageert met 13,6 g zuurstof om monoxide te vormen Welke hoeveelheid gram zou hetzelfde dioxide reageren?
Inzicht in de reacties
* Reactie 1:koolstof + zuurstof → koolmonoxide (CO)
* Reactie 2:koolstof + zuurstof → kooldioxide (co₂)
Key Concepts
* Masswetwet: In een chemische reactie is de totale massa van de reactanten gelijk aan de totale massa van de producten.
* stoichiometrie: De studie van de kwantitatieve relaties tussen reactanten en producten in chemische reacties.
Het probleem oplossen
1. Bepaal de mol zuurstof:
* De molaire zuurstofmassa (o₂) is 32 g/mol.
* Mol zuurstof =(13,6 g) / (32 g / mol) =0,425 mol
2. Vind de mol koolstof:
* Bij de vorming van koolmonoxide (CO) is de verhouding tussen koolstof en zuurstof 1:1.
* Daarom reageerde 0,425 mol koolstof met de zuurstof.
3. Bereken de massa koolstof:
* De molaire koolstofmassa (C) is 12 g/mol.
* Massa van koolstof =(0,425 mol) * (12 g/mol) =5,1 g
4. Bepaal de mol zuurstof die nodig is voor koolstofdioxide:
* Bij de vorming van koolstofdioxide (CO₂) is de verhouding van koolstof en zuurstof 1:2.
* Omdat we 0,425 mol koolstof hebben, hebben we tweemaal de hoeveelheid zuurstof nodig voor CO₂.
* Mol zuurstof nodig voor co₂ =0,425 mol * 2 =0,85 mol
5. Bereken de massa zuurstof die nodig is voor koolstofdioxide:
* Massa van zuurstof nodig voor co₂ =(0,85 mol) * (32 g/mol) =27,2 g
Antwoord:
Dezelfde koolstofmassa zou reageren met 27,2 gram van zuurstof om koolstofdioxide te vormen.
 Een soort die een Envirmoent binnenkomt waar het nog niet eerder heeft gewoond, wordt een genoemd?
Een soort die een Envirmoent binnenkomt waar het nog niet eerder heeft gewoond, wordt een genoemd?  Appalachia ondergrondse aardgasopslag doorstaat eerste test
Appalachia ondergrondse aardgasopslag doorstaat eerste test Nieuw onderzoek onthult effect van opwarming van de aarde op het smelten van Groenlandse ijs
Nieuw onderzoek onthult effect van opwarming van de aarde op het smelten van Groenlandse ijs Trans-Brazilië parcours wekt hoop voor de toekomst van Atlantisch Woud
Trans-Brazilië parcours wekt hoop voor de toekomst van Atlantisch Woud Wat is een effect dat Nutation kan hebben op het aardklimaat?
Wat is een effect dat Nutation kan hebben op het aardklimaat?
Hoofdlijnen
- Big data helpt onderzoekers in de strijd om plantenindringers onder controle te krijgen
- Hoe jaloezie werkt
- Wat is de taxonomie van een alligator?
- Wat is een andere celnaam voor transplantaatafstotcellen?
- Hoe beïnvloedt menselijke activiteit de organismen en het aardoppervlak?
- Onderzoekers onthullen hoe genetisch identieke watervlooien zich ontwikkelen tot verschillende geslachten
- Trechtervisie:nieuwe informatie over hoe cellen in het oog helpen licht naar het netvlies te geleiden
- Zijn prokaryotische cellen het type waaruit planten en dieren vormen?
- Wat is menselijke selectie?
- Na 90 jaar, wetenschappers onthullen de structuur van benzeen
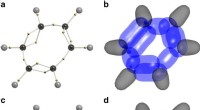
- De universele waarheid over plakkerige oppervlakken

- Cellulose voor het vervaardigen van geavanceerde materialen

- Een snelle malariatestkit die de diagnose in ontwikkelingslanden kan helpen

- Eenkristaltechnologie belooft veel voor lithium-ionbatterijen van de volgende generatie

 Het spliceosoom - nu beschikbaar in hoge definitie
Het spliceosoom - nu beschikbaar in hoge definitie Wat is de juiste maat van een astronomische eenheid?
Wat is de juiste maat van een astronomische eenheid?  Was Mercury 1 de eerste NASA -missie?
Was Mercury 1 de eerste NASA -missie?  Overstappen naar een schone economie kan Australië honderden miljarden besparen, vondsten melden
Overstappen naar een schone economie kan Australië honderden miljarden besparen, vondsten melden Welke twee dingen moet je weten om de snelheid te bepalen?
Welke twee dingen moet je weten om de snelheid te bepalen?  Groep:VS, Rusland blokkeert consensus tijdens bijeenkomst over moordende robots
Groep:VS, Rusland blokkeert consensus tijdens bijeenkomst over moordende robots Een pad naar schoon drinkwater voor alle Californiërs
Een pad naar schoon drinkwater voor alle Californiërs Hoe sociale media de menselijke beschaving hebben gesynchroniseerd
Hoe sociale media de menselijke beschaving hebben gesynchroniseerd
- Elektronica
- Biologie
- Zonsverduistering
- Wiskunde
- French | Italian | Spanish | Portuguese | Swedish | German | Dutch | Danish | Norway |
-
Wetenschap © https://nl.scienceaq.com