Wetenschap
Where do chemical reactions occur in electrochemical cells?
Hier is een uitsplitsing:
* Anode: The electrode where oxidation occurs (loss of electrons).
* Cathode: De elektrode waar reductie optreedt (versterking van elektronen).
The specific reactions happening at each electrode depend on the type of electrochemical cell:
* Galvanic Cells (Battery): These cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy.
* The anode is the negative electrode, and the cathode is the positive electrode.
* De oxidatiereactie bij de anode biedt elektronen die door een extern circuit naar de kathode stromen, waar ze worden gebruikt in de reductiereactie.
* Electrolytic Cells: These cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions.
* The anode is the positive electrode, and the cathode is the negative electrode.
* An external power source pushes electrons from the anode to the cathode, forcing the oxidation and reduction reactions to occur.
Samenvattend:
Elektrochemische cellen zijn ontworpen om oxidatie- en reductiereacties te scheiden om elektrische energie (galvanische cellen) te genereren of niet-spontane chemische reacties (elektrolytische cellen) aan te dringen. These reactions happen at the electrodes:the anode for oxidation and the cathode for reduction.
 Hoe groenere biobrandstoffen te maken
Hoe groenere biobrandstoffen te maken  Wat maakt een kiemwortel anders dan een molecuul?
Wat maakt een kiemwortel anders dan een molecuul?  De rol van de bovenbouw bij spanningsverlies in de eerste cyclus in lithium-ionbatterijen
De rol van de bovenbouw bij spanningsverlies in de eerste cyclus in lithium-ionbatterijen Is gas een chemisch synoniem voor het woord bruisen?
Is gas een chemisch synoniem voor het woord bruisen?  Op schelpen geïnspireerde suikerschild beschermt materialen in vijandige omgevingen
Op schelpen geïnspireerde suikerschild beschermt materialen in vijandige omgevingen
 Welke fysieke effecten hebben tornado's op dieren in het wild?
Welke fysieke effecten hebben tornado's op dieren in het wild?  Dood hout in de wereldwijde koolstofcyclus
Dood hout in de wereldwijde koolstofcyclus Californische mijlpaal:4 miljoen hectare verbrand door bosbranden
Californische mijlpaal:4 miljoen hectare verbrand door bosbranden Het VK verspilt elk jaar miljoenen tonnen voedsel - hier kunnen we verandering in brengen
Het VK verspilt elk jaar miljoenen tonnen voedsel - hier kunnen we verandering in brengen Onderzoekers ontwikkelen systeem voor vroegtijdige waarschuwing voor watervervuiling met behulp van kleine watervlooien
Onderzoekers ontwikkelen systeem voor vroegtijdige waarschuwing voor watervervuiling met behulp van kleine watervlooien
Hoofdlijnen
- Werkt de gramkleuringsprocedure voor alle bacteriën?
- Nieuw onderzoek toont aan dat micro-organismen in de bodem extra broeikasgasemissies kunnen veroorzaken door het ontdooien van permafrost
- Wat zijn hormonale stimuli?
- Is het Mexicaanse gen sterker dan het Filipijnse gen?
- Evolutiebiologen laten zien dat de kleurvarianten van vrouwelijke koekoeken gebaseerd zijn op oude mutaties
- Welke monosacharide is een bouwsteen van de muur van de plantencel?
- Wat zijn onderwaterorganismen?
- Indringende vraag:Waarom overleefden zoogdieren het 'K/T-uitsterven'?
- Hoe reproduceren parameciums zich?
- Onderzoeksteam ontdekt verloren afbeeldingen uit de 19e eeuw

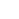
- De reisroute van protonen in polymeren kan de weg wijzen naar schone brandstoffen
- Technologie verandert smartphones in on-the-spot detectoren voor door voedsel overgedragen ziekten, andere gevaarlijke verontreinigingen

- Grote doorbraak in de productie van rode bloedcellen
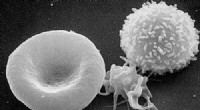
- Induced-fit adsorbens voor acetyleen
 Startup heeft tot doel de supply chain van lithium-ionbatterijen op te schonen
Startup heeft tot doel de supply chain van lithium-ionbatterijen op te schonen Een natuurkundig perspectief op wondgenezing
Een natuurkundig perspectief op wondgenezing Wat is een taak van sekscel?
Wat is een taak van sekscel?  Waarom moeten chemici de factoren kennen die de reactiesnelheden beïnvloeden?
Waarom moeten chemici de factoren kennen die de reactiesnelheden beïnvloeden?  Waarom kun je de maan soms wel en niet zien?
Waarom kun je de maan soms wel en niet zien?  Hoe bacteriën een enzym bouwen dat klimaatveranderend lachgas vernietigt
Hoe bacteriën een enzym bouwen dat klimaatveranderend lachgas vernietigt Nieuw composietmateriaal op basis van aluminium en samariumhexaboride met bijna nul uitzetting
Nieuw composietmateriaal op basis van aluminium en samariumhexaboride met bijna nul uitzetting Astronomen ontdekken klasse van vreemde objecten in de buurt van het enorme zwarte gat van ons melkwegstelsel
Astronomen ontdekken klasse van vreemde objecten in de buurt van het enorme zwarte gat van ons melkwegstelsel
- Elektronica
- Biologie
- Zonsverduistering
- Wiskunde
- French | Italian | Spanish | Portuguese | Swedish | German | Dutch | Danish | Norway |
-
Wetenschap © https://nl.scienceaq.com