Wetenschap
What does the hydrolysis of lipid molecules yield?
* glycerol: This is a three-carbon alcohol molecule.
* vetzuren: Dit zijn lange ketens van koolwaterstoffen met een carboxylgroep aan één uiteinde. Het aantal koolstofatomen in de keten en de aanwezigheid van dubbele bindingen bepalen het type vetzuur (bijvoorbeeld verzadigd, enkelvoudig onverzadigd, meervoudig onverzadigd).
* Water: This is used as a reactant in the hydrolysis reaction.
The hydrolysis of triglycerides is catalyzed by enzymes called lipases . This process is essential for the body to break down fats for energy and to absorb them from the digestive system.
Here's a simplified equation to illustrate the process:
Triglyceride + 3 Water → Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids
It's worth noting that hydrolysis can also be applied to other types of lipids, such as phospholipids. However, the specific products will vary depending on the type of lipid being hydrolyzed.
 Wetenschappers ontdekken het mechanisme van luminescentie van schimmels en creëren luminescente gisten
Wetenschappers ontdekken het mechanisme van luminescentie van schimmels en creëren luminescente gisten Hoeveel valentie -elektronen bezit GA?
Hoeveel valentie -elektronen bezit GA?  Veroorzaken dochters werkelijk echtscheidingen? Misschien niet
Veroorzaken dochters werkelijk echtscheidingen? Misschien niet  Wat zijn de drie soorten niet -metalen ophanging?
Wat zijn de drie soorten niet -metalen ophanging?  Wat is de vergelijking voor de reactie van 2-naftol en natriumhydroxide?
Wat is de vergelijking voor de reactie van 2-naftol en natriumhydroxide?
 Westelijkste provincie van Canada roept noodtoestand uit vanwege bosbranden
Westelijkste provincie van Canada roept noodtoestand uit vanwege bosbranden Wat is de onveranderlijke laatste fase van een ecosysteem?
Wat is de onveranderlijke laatste fase van een ecosysteem?  Een appel die uit een boom viel, hielp Sir Isaac Newton met wat te bedenken?
Een appel die uit een boom viel, hielp Sir Isaac Newton met wat te bedenken?  Planten en dieren die Lewis & Clark ontdekten in de Louisiana Purchase
Planten en dieren die Lewis & Clark ontdekten in de Louisiana Purchase  De impact van de gebouwen van een stad op het weer meten
De impact van de gebouwen van een stad op het weer meten
Hoofdlijnen
- Wat zijn de vrouwelijke reproductieve structuren van een plant?
- De kleinste biologische totdat dat in de loop van de tijd kan evolueren, is?
- Virussen worden niet geclassificeerd als levende organismen omdat ze geen levensprocessen uitvoeren, behalve?
- Hoe organiseren wetenschappers?
- Welk chromosoom beïnvloedt de ziekte van Tay-Sachs?
- Exon: definitie, functie en belang in RNA Splicing
- Wat is een organisme dat geen eigen voedsel kan maken?
- Wat zijn de basisvormen van bacteriecellen?
- Hoe kloon je een organisme?
- Hoge magnetische velden regelen zowel de snelheid als het product van chemische reacties

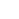
- Moleculaire schakelaar detecteert metalen in de omgeving
- Biomateriaal kan tand in leven houden na wortelkanaalbehandeling

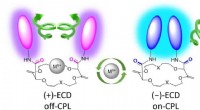
- Onderzoekers ontwikkelen thermo-responsieve eiwithydrogel
- Moleculaire bindingen smeden met groen licht

 Nieuwe numerieke methode maakt simulatie van aardverschuivingstsunami's mogelijk
Nieuwe numerieke methode maakt simulatie van aardverschuivingstsunami's mogelijk Wat is het gewicht van Europa in vergelijking met de aarde?
Wat is het gewicht van Europa in vergelijking met de aarde?  NASA's GPM onderzoekt zwakkere tropische storm Yutus-regenval
NASA's GPM onderzoekt zwakkere tropische storm Yutus-regenval Wat zijn drie doelorganen van het parathyroïde hormoon?
Wat zijn drie doelorganen van het parathyroïde hormoon?  Hoe breng je een formule in evenwicht met fluor uranium koolstof en kalium?
Hoe breng je een formule in evenwicht met fluor uranium koolstof en kalium?  Welke thermische energie wordt overgedragen van de ene substantie naar de andere het roept wat?
Welke thermische energie wordt overgedragen van de ene substantie naar de andere het roept wat?  Zijn gasplaneten bevroren als ijskristallen?
Zijn gasplaneten bevroren als ijskristallen?  Hoe worden meteoren gemeten?
Hoe worden meteoren gemeten?
- Elektronica
- Biologie
- Zonsverduistering
- Wiskunde
- French | Italian | Spanish | Portuguese | Swedish | German | Dutch | Danish | Norway |
-
Wetenschap & Ontdekkingen © https://nl.scienceaq.com